(h, k)
half-life
horizontal shift
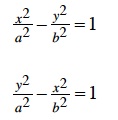
hyperbola
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | JKL | MN | O | P | Q | R | S | T | UV | WXYZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algebra 2 Connections Glossary | ||||||||||||||||||
(h, k) |
|
|---|---|
| In this course h and k are used as parameters in general equations for families of functions f(x) = af(x − h) + k and families of relations to represent the horizontal and vertical shifts of the parent graph. The point (h, k) represents location of a point that corresponds to (0, 0) for parent graphs where (0, 0) is on the graph. For circles, ellipses, and hyperbolas, (h, k) represents the center of the shifted graph. (pp. 190, 207, 576, 585) | |
half-life |
|
| When material decays, the half-life is the time it takes until only half the material remains. (p. 131) | |
horizontal shift |
|
Used with parent graphs and general equations for functions and relations such as y = a(x − h)2 + k. It is the amount a graph is moved left or right in relation to its parent graph, in this case y = x2. The horizontal shift will be h units to the right if h is positive, to the left if h is negative. (p. 175)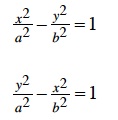 |
|
hyperbola |
|
| A hyperbola has relationships corresponding to those of an ellipse. A hyperbola is made up of two branches. The line connecting the vertices of the two branches is called the transverse axis, and the letter a is used to represent the distance from the center to either vertex. For the equation at top right the center of the hyperbola is at the origin. The vertices are (±a, 0) and the asymptotes have the
equations
| |
hypotenuse |
|
|---|---|
| The longest side of a right triangle, the side opposite the right angle.
|
|