measure of central tendency
median
midpoint
mixed number (fraction)
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
measure of central tendency |
|
|---|---|
| Mean, median, and mode are all measures of central tendency, reflecting special statistical information about a set of data. | |
median |
|
| The middle number of an ordered set of data. If there is no distinct middle, then the average of the two middle numbers is the median. | |
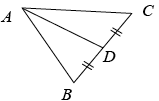
midpoint |
|
A point that divides a segment into two segments of equal length. For example, D is the midpoint of BC in  |
|
mixed number (fraction) |
|
| A number that consists of an integer and a fraction. For example, |
|
mode |
|
| The number or numbers that occur the most often within a set of data. There may be more than one mode for a set of data. | |
multiple |
|
| The product of a whole number and any other (nonzero) whole number. For example, 15 is a multiple of 5. | |
multiplication (·) |
|
| An operation that reflects repeated addition. For example, 3 · 4 = 4 + 4 + 4. | |
multiplicative identity |
|
| The multiplicative identity property states that multiplying any expression by 1 leaves the expression unchanged. That is, a(1) = a. For example, 437 x · 1 = 437x. | |