scientific notation
sector
semi-circle
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
scale (scaling) |
|
|---|---|
| The ratio between a length of the representation (such as a map, model, or diagram) and the corresponding length of the actual object. For example, the map of a city may use one inch to represent one mile. | |
scale factor |
|
| A ratio that compares the sizes of the parts of one figure or object to the sizes of the corresponding parts of a similar figure or object. | |
scalene triangle |
|
| A triangle with no congruent sides. | |
scatterplot |
|
| Two related sets of data may have the corresponding values of the sets listed as ordered pairs. If these ordered pairs are graphed in the coordinate plane, then the result is a scatterplot. (Also see negative correlation and positive correlation.) | |
scientific notation |
|
| A number is expressed in scientific notation when the number is in the form a · 10n, where 1 ≤ a < 10 and n is an integer. For example, the number 31,000 may be expressed in scientific notation as 3.1 · 104. | |
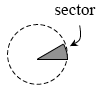
sector |
|
A region formed by two radii of a central angle and the arc between the endpoints of the radii on the circle. The shaded portion of the drawing below is a sector.

|
|
semi-circle |
|
| In a circle, a semicircle is an arc with endpoints that are endpoints of any diameter of the circle. A semi-circle is a half circle and has a measure of 180º. | |
set |
|
| A collection of items. | |
similar figures |
|
Similar figures have the same shape but are not necessarily the same size. For example, the two triangles below are similar. In similar figures, the measures of corresponding angles are equal and the lengths of corresponding sides are proportional.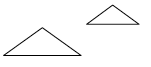 |
|
simple interest |
|
| Interest that is paid only on the principal (the amount originally invested). Simple interest is found by multiplying the principal, the rate, and the amount of time. | |
simplest form of a fraction |
|
|---|---|
| A fraction for which the numerator and the denominator have no common factor greater than one. | |
simplify |
|
| To simplify an expression is to write a less complicated expression with the same value. A simplified expression has no parentheses and no like terms. For example, the expression 3 − (2x + 7) − 4x may be simplified to − 4 − 6x. When working with algebra tiles, a simplified expression uses the fewest possible tiles to represent the original expression. | |
skew lines |
|
| Lines that do not lie in the same flat surface. | |
slope |
|
A ratio that describes how steep (or flat) a line is. Slope may be positive, negative, or even zero, but a straight line has only one slope. Slope is the ratio 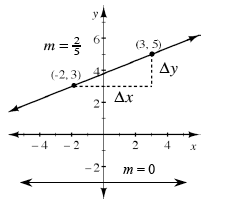 |
|
solution |
|
| The number or numbers that when substituted into an equation or inequality make the equation or inequality true. For example, x = 4 is a solution to the equation 3x − 2 = 10 because 3x − 2 equals 10 when x = 4. A solution to a two-variable equation is sometimes written as an ordered pair (x, y) . For example, x = 3 and y = − 2 is a solution to the equation y = x − 5 . This solution may be written as (3, − 2).
|
|
square |
|
A quadrilateral with four right angles and four congruent sides.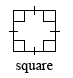 |
|
square measure |
|
| The units used to describe the measure of an area in the form of 1 x 1 unit squares. | |
square number |
|
| The numbers in the pattern 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, …. That is, the squares of the counting numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … are known as square numbers. | |
square root ( |
|
| A number a is the square root of b if a2 = b and a ≥ 0. The square root of 9 ( |
|
stem-and-leaf plot |
|
A way of displaying data values that is made by arranging the data with the vertical “stem” consisting of the first digits of the data and the horizontal “leaves” that show the remaining digits.
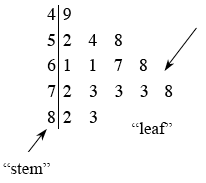 |
|
straight angle |
|
|---|---|
An angle that measures 180º. This occurs when the rays of the angle point in opposite directions, forming a line.
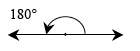 |
|
subproblems |
|
| A problem solving strategy which breaks a problem into smaller parts which must be solved in order to solve the original, more complex problem. | |
substitution |
|
| Replacing one symbol with a number, a variable, or another algebraic expression of the same value. Substitution does not change the value of the overall expression. For example, suppose that the expression13x − 6 must be evaluated for x = 4. Since x has the value 4, 4 may be substituted into the expression wherever x appears, giving the equivalent expression 13(4) − 6. | |
subtraction (–) |
|
| An operation that gives the difference between two numbers. | |
sum |
|
| The result of adding two or more numbers. For example, the sum of 4 and 5 is 9. | |
supplementary angles |
|
Two angles A and B for which A + B = 180°. Each angle is called the supplement of the other. In the example below, angles A and B are supplementary. Supplementary angles are often adjacent. For example, since 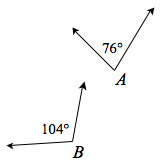  |
|
surface area |
|
| The sum of all the area(s) of the surface(s) of a three-dimensional solid. For example, the surface area of a cylinder is the sum of the areas of its top base, its bottom base, and its vertical or slant surfaces. | |